What Is High Blood Pressure?
If you have high blood pressure, you’ll probably experience no signs or symptoms of the condition, even if you have extremely high blood pressure.
In very rare cases, and if blood pressure reaches dangerous levels, a person may get headaches or more nosebleeds than normal.
But in the majority of cases, there are no signs or symptoms of hypertension — which is why it has been dubbed the “silent killer” — so it’s important to understand how to tell if you have high blood pressure.
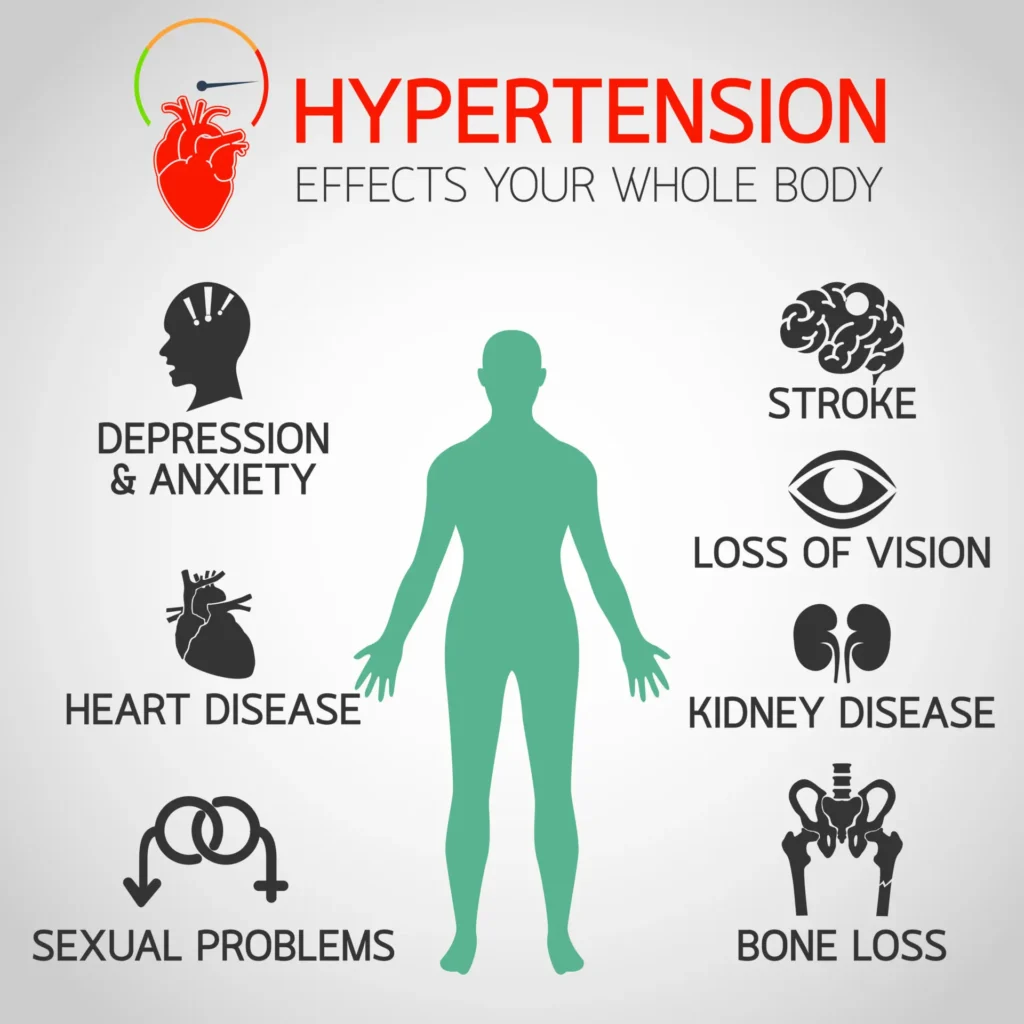
If high blood pressure goes undetected for a long period, the condition can damage your heart, blood vessels, kidneys, and other parts of your body.
For some people, it takes being diagnosed with coronary heart disease, stroke, or kidney failure to learn that they also have high blood pressure.
How Is High Blood Pressure Diagnosed?
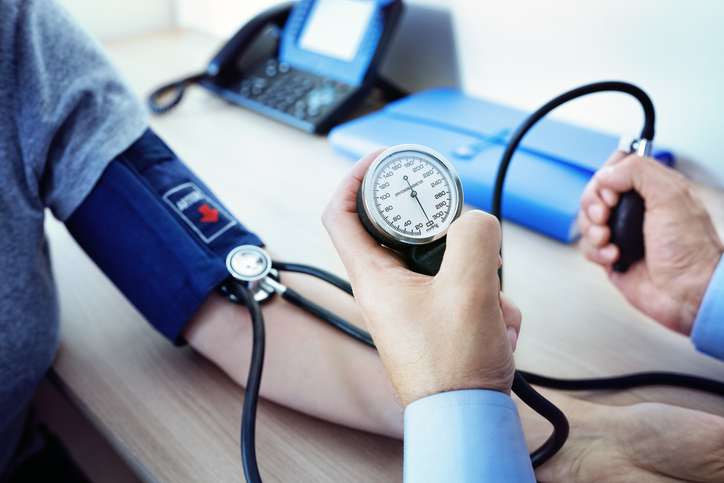
The only way to determine if you have high blood pressure is to have it tested. It is an easy and painless test and can be done in your doctor’s office.
To be prepared for the test:
- Avoid drinking coffee or smoking cigarettes for 30 minutes before the test.
- Go to the bathroom before the test.
- Sit for five minutes before being tested.
A gauge, stethoscope, and a blood pressure cuff are often used to measure your blood pressure.
While you’re sitting down, your healthcare provider will wrap an inflatable arm cuff around your arm and measure your blood pressure using a pressure-measuring gauge. Throughout the test, try to avoid moving your arm.
Since your blood pressure varies throughout the day, your doctor will most likely take two to three blood pressure readings during your visit at three or more separate appointments to confirm that it’s elevated.
Your doctor may also measure your blood pressure in both arms to see if there is a difference.
Blood pressure readings include two numbers, given in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
The first number measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats (contracts). This is called systolic pressure.
The second number measures the pressure in your arteries between beats (when your heart is relaxed and filling with blood). This is called diastolic pressure.
Blood pressure measurements fall into the following five categories:
Normal Blood Pressure Blood pressure below 120/80 mmHg is considered normal. Once you get above this range, your risk of cardiovascular disease increases.
Elevated Blood Pressure When the readings consistently range from 120 to 129 mmHg systolic and less than 80 mmHg diastolic, it is called elevated. People with elevated blood pressure are at an increased risk for developing high blood pressure and should take steps to control it, including following a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.
Hypertension Stage 1 This is when blood pressure consistently ranges from 130 to 139 mmHg systolic or 80 to 89 mmHg diastolic. Patients who have hypertension stage 1 will likely be prescribed lifestyle modifications to lower blood pressure. Medication may also be considered based on your risk of cardiovascular disease.
Hypertension Stage 2 This is when blood pressure is consistently 140/90 mmHg or higher. At this stage, doctors are likely to prescribe medication to lower blood pressure in conjunction with lifestyle changes.
Hypertensive Crisis This is a level of high blood pressure that requires medical attention. Should your blood pressure measurement be 180/120 mm Hg, wait five minutes before retesting. If it remains elevated, consult your physician without delay. If blood pressure exceeds 180/120 mm Hg and you experience chest pain, dyspnoea, back pain, numbness and weakness, visual disturbances, or speech difficulties, you may be suffering from organ damage and should contact emergency services immediately.
What Other Tests Will I Need?
If you have high blood pressure, your doctor may also order the following tests to check for more signs of heart disease:
- Urine test
- Blood tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Cholesterol test
Taking Your Blood Pressure
To get more accurate readings of your blood pressure, your doctor may ask you to record your blood pressure at home and work with your automated blood pressure monitor.
Doing so can help determine if treatment is working, or if your condition is getting worse.
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends an automatic, cuff-style upper arm monitor for at-home use.
Before measuring your blood pressure, do not smoke, drink caffeinated beverages, or exercise for at least 30 minutes before the test. Rest for at least five minutes before the measurements and sit still with your back straight and supported. The feet should be flat on the floor and not crossed. Your arm should also be supported on a flat surface like a table with the upper arm at heart level.
Follow the instructions that come with your monitor or are provided by your healthcare provider.
Take readings at the same time every day, take two to three each time about a minute apart, and then record your results.
Finally, make sure not to take measurements over clothing.